השירות של דינו.
שאלון מותאם משתמש
בלי לחשוב "מאיפה להתחיל" ומה לכתוב. פשוט לענות על השאלון לפי סוג התביעה הקטנה, והוא יתקדם בהתאם לקצב ולתשובות שלך.
14 דקות והתביעה הקטנה מוכנה
מענה על השאלון במערכת אורך כ-14 דקות בממוצע. הפקת התביעה אורכת דקה בלבד.
מותאם להוראות הרשות השופטת
כ-50% מהתביעות הקטנות נדחות בגלל כשלים טכניים(!) כתב התביעה של דינו, מותאם להוראות מנהל בתי המשפט.
חיסכון של יותר מ-75% בעלויות
גם אם התביעה שלכם קטנה, אנשי מקצוע לוקחים כסף גדול.
שאלות נפוצות.
איך מגישים תביעה קטנה? ריכזנו את כל מה שצריך לדעת על המשך התהליך- הגשת תביעה קטנה.
דינו מעדיף לשמור על פרטיות בעניין. אבל תמיד אפשר לנסות 😉
הפקת תביעה קטנה באמצעות המערכת עולה 299 ש"ח. אם תרצו שנגיש את כתב התביעה עבורכם באמצעות שליח משפטי, תתווסף עמלת הגשה בסך 150 ש"ח. כך או כך, כשמגישים את כתב התביעה לבית-המשפט, יש לשלם לבית-המשפט אגרה של 1% או 50 ₪, לפי הגבוה מהשניים. כלומר, על תביעות עד 5,000 ₪ תשולם אגרה בסך 50 ₪, והחל מ-5,001 ₪ האגרה תעמוד על 1% מסכום התביעה.
או בקיצור, לחצו כאן למחשבון עלויות.
המערכת מאובטחת מאוד! מעבר לאבטחה השוטפת של האתר והמערכת, התקנו ככלי אבטחה נוסף, סיסמה מורכבת ואישית לכל משתמש/ת שאינה חשופה לאיש מלבדו/ה. כמובן שבאחריות המשתמש לנהוג בסיסמה בחכמה ולמנוע מצדדים שלישיים גישה – עקיפה או ישירה – לסיסמה שקיבל.
בנוסף, התשלום מבוצע בדף מאובטח של חברת הסליקה, בתקן האבטחה המתקדם PCI. לחברות האשראי המובילות (ישראכארט ו-ויזה) ישנו גם מנגנון אבטחה נוסף (3D-SECURE) אשר שולח למשתמש קוד אישי זמני לנייד/למייל כדי לוודא שאכן הוא זה שמבצע את העסקה.לפרטים נוספים ראו את מדיניות הפרטיות שלנו.
המשתמשים בדינו יקבלו את ההודעות הבאות (שאינן דבר-פרסומת): (1) רישום למערכת וקבלת סיסמה; (2) כתב התביעה הקטנה מוכן; (3) כתב התביעה הוגש; (4) תקלה הנוגעת לתהליך הפקת והגשת כתב התביעה; (5) מענה לקריאת שירות שהמשתמש/ת פתח/ה או מענה לפניות; (6) חשבונית עסקה בגין התשלום (שנשלחת ישירות מספק הסליקה); (7) סקר חוויית שירות כדי שנדע מה לשמר ומה לשפר.
ככול שיחול שינוי מהותי במדיניות הפרסומים שלנו, אנו כמובן נבקש את הסכמת המשתמש/ת מראש. להרחבה ניתן לעיין במדיניות הפרטיות שלנו.
כן, ניתן לבצע שינויים לאחר הפקת התביעה. לאחר הפקת התביעה, ניתן לפתוח קריאת שירות בנושא "שינויים בתביעה לפני הגשה" ולתאר את הבעיה או השינוי המבוקש.
כתב התביעה יהיה זמין לצפייה רק לאחר התשלום ואישור חברת האשראי כי התשלום הועבר בהצלחה. עם זאת, תשובות המשתמש לשאלון תהיינה זמינות לצפייה ועריכה לפני התשלום. כתב התביעה יחולל כמסמך Word ולאחר הורדתו למחשב, ניתן לעריכה חופשית.
כתב התביעה זמין להורדה בכל עת באזור האישי. בנוסף, מומלץ לבדוק אם הודעת הדוא"ל הגיעה לתיבת הספאם. אם שני המקרים לא עזרו, מומלץ לבקר בעמוד "איך זה עובד" באתר וכן כמובן, ניתן לפנות אלינו ישירות.
נתונים.
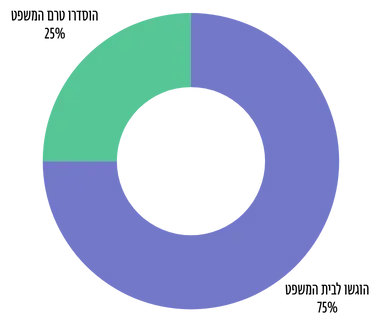
כ- 25% מהתביעות הקטנות המוגשות דרכינו, נסגרות בפשרה טרם ההגעה לבית המשפט.
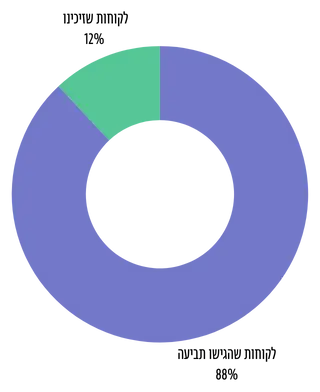
כ- 12% מהלקוחות שלנו זוכו באופן מלא (טרם הגשת התביעה) כיוון שלא היה להם קייס.
יש לנו את זה?
דינו מביא בשורה בתחום התביעות הקטנות בישראל! שברנו את מחירי השוק, ואנחנו חוסכים ללקוחות שלנו המון זמן וכאב ראש.
עם דינו, אין תביעה קטנה מידי.

